
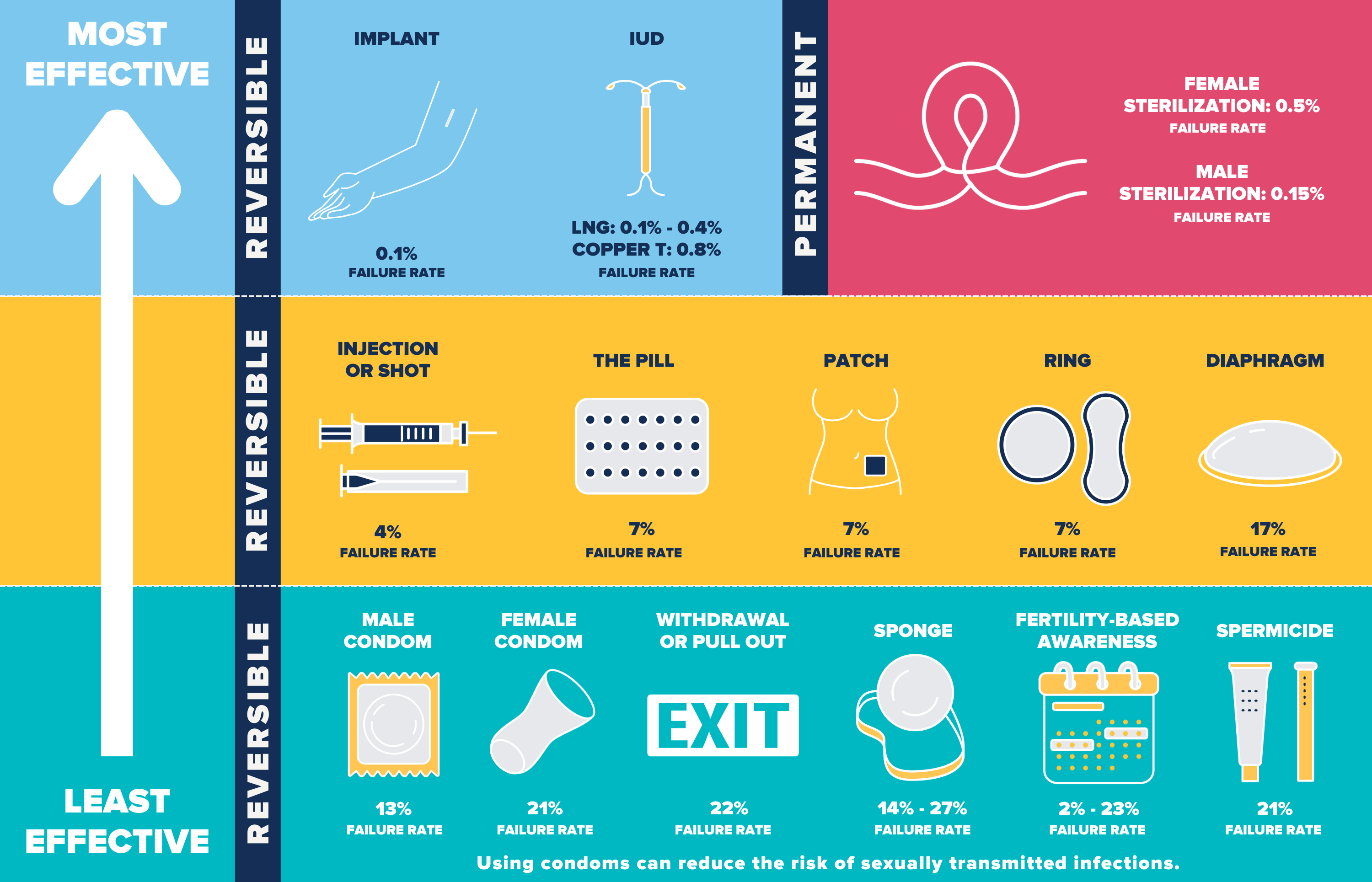
Birth control (contraception) can prevent a pregnancy.
There are many different forms of birth control. Some require seeing a health care provider and others are available over the counter. See the table below for more details.
Did you know?
If you live in California, you have options for free or low-cost birth control, regardless of immigration status.
let’s talk about
BIRTH CONTROL BENEFITS
Birth control can be used for more than preventing pregnancy.
Using condoms can prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Among females who use birth control, some use it only to prevent pregnancy. Others use it for the benefits. And many use it for both. The birth control pill can prevent you from becoming pregnant, but can also make your menstrual cycles regular, decrease cramps during your period, decrease your menstrual flow and risk for ovarian cancer. The IUD with progestin decreases your menstrual flow, sometimes even stopping your period, and can protect against endometrial cancer. The Depo Provera shot can help with endometriosis and heavy periods. It’s important to speak to your health care provider to see what is best for you.
- Lighter or regular periods
- Reduces menstrual cramps
- Helps with acne
- Lowers risk of some cancers
- Prevents cysts in ovaries
While there are benefits to birth control that extend beyond prevention of pregnancy, there are also increased risks associated with some types of birth control. It’s important to choose the birth control that’s best for you and your health.
explore
YOUR OPTIONS
Choose the best birth control for you
(consistency is key)

Top
Sterilization
Duration: Permanent
Cost, Male: $0 – $1,300
Cost, Female: $0 – $6,000
Maintenance Level: Lasts for life
Effectiveness: 99%
Risks, Male: Pain, bleeding, infection
Risks, Female: Pain, bleeding, infection, complications after surgery

Top
Implant
Duration: Up to 5 years
Cost: $0 – $1,300
Maintenance Level: Low
Effectiveness: 99%
Risks: Menstrual changes, mood swings or depressed mood, weight gain, headaches, acne

IUD
IUD
Duration: 3-12 years
Cost: $0 – $1,300
Maintenance Level: Low
Effectiveness: 99%
Risks, Copper IUD: Cramps, heavier/longer periods, spotting between periods
Risks, IUD with Progestin: Irregular bleeding, no periods, abdominal or pelvic pain
IUD
Injection or Shot
Duration: 3 months
Cost: $0 – $150
Maintenance Level: Scheduled
Effectiveness: 96%
Risks: Loss of bone density, irregular bleeding/bleeding between periods, headaches, weight gain, nervousness, dizziness, abdominal discomfort

IUD
The Pill
Duration: Daily
Cost: $0 – $50
Maintenance Level: Scheduled
Effectiveness: 93%
Risks: Spotting/bleeding between periods, nausea, breast tenderness, headaches

IUD
Patch
Duration: Weekly
Cost: $0 – $150
Maintenance Level: Scheduled
Effectiveness: 93%
Risks: Spotting/bleeding between menstrual periods, nausea, stomach pain, breast tenderness, headaches, skin irritation

IUD
Ring
Duration: Monthly
Cost: $0 – $200
Maintenance Level: Scheduled
Effectiveness: 93%
Risks: Vaginal discharge/discomfort in the vagina/mild irritation, headaches, mood changes, nausea, breast tenderness

IUD
Diaphragm
Duration: Per encounter
Cost: $0 – $75
Maintenance Level: Use every time
Effectiveness: 87%
Risks: Allergic reaction, urinary tract infection

IUD
Male Condom
Duration: 3-12 years
Cost: $0 – $1,300
Maintenance Level: Low
Effectiveness: 87%
Risks: Irritation, allergic reactions

IUD
Female Condom
Duration: Per encounter
Cost: $0 – $3
Maintenance Level: Use every time
Effectiveness: 87%
Risks: Discomfort or pain during insertion or sex, burning sensation, rash, or itching

IUD
"Pull Out" or Withdrawal
Duration: Per encounter
Cost: Free
Maintenance Level: Use every time
Effectiveness: 78%
Risks: No direct risks

IUD
Sponge
Duration: Per encounter
Cost: $0 – $15
Maintenance Level: Use every time
Effectiveness: 79-86%
Risks: Loss of bone density, irregular bleeding/bleeding between periods, headaches, weight gain, nervousness, dizziness, abdominal discomfort

IUD
Fertility-Based Awareness
Duration: Per encounter
Cost: $0 – $20
Maintenance Level: Use every time
Effectiveness: 77-98%
Risks: No direct risks

IUD
Spermicide
Duration: Per encounter
Cost: $0 – $270
Maintenance Level: Use every time
Effectiveness: 79%
Risks: Irritation, allergic reactions, urinary tract infection
let’s talk
PRICING
Californians have many options for free or low-cost birth control, regardless of immigration status.
You can also reference the Besider.org search tool to find birth control options by zip code.
First
Covered California

Covered California plans provide up to a 12-month free supply of FDA-approved birth control, including the ring, patch or oral birth control pills. Most employer-based health insurance plans also cover this service.
First
Family PACT

Family PACT provides free birth control If you are low income, but do not qualify for Medi-Cal.
First
Medi-Cal

Medi-Cal plans provide free birth control through any Medi-Cal provider.
First
Private Health Insurance
If you have private health insurance, it’s important to know that through the Affordable Care Act, contraception is a covered benefit. Plans in the Health Insurance Marketplace® must cover contraceptive methods and counseling for all women, as prescribed by a health care provider.
Plans must cover these services without charging a copayment or coinsurance when provided by an in-network provider — even if you haven’t met your deductible.
Covered Contraceptive Methods
FDA-approved contraceptive methods prescribed by a woman’s doctor are covered, including:
- Barrier methods, like diaphragms and sponges
- Hormonal methods, like birth control pills and vaginal rings
- Implanted devices, like intrauterine devices (IUDs)
- Emergency contraception, like Plan B® and ella®
- Sterilization procedures
- Patient education and counseling
Plans aren’t required to cover drugs to induce abortions and services for male reproductive capacity, like vasectomies.
If you do not have health insurance…
Or if you do not use your insurance, you may be eligible to become a Family PACT client and find a provider through their Provider Search Tool.
let’s answer your
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
First
Can I get birth control without a doctor’s prescription?
Yes. In California, you can purchase (without a prescription) hormonal birth control methods you can administer yourself like the pill, patch, or ring, from a pharmacist. A pharmacy that keeps birth control in stock is required under California law to give patients timely access to them and cannot prevent you from obtaining birth control.
I’m a minor. Can I get birth control?
Yes. California Family Code § 6925 allows for minors to receive birth control without parental or guardian consent. There is also no age restriction and the health care provider is not allowed to inform a parent or legal guardian without the minor’s consent.
What about religious employers and access to birth control?
While health care providers and pharmacists cannot deny access to birth control based on religious or personal beliefs, an employer’s legal rights differ. Religious employers may be able to request health insurance plans that do not cover approved contraceptive methods. SB 523 (Leyva) expands birth control access – regardless of gender or insurance coverage status – by requiring health plans to cover certain over-the-counter birth control without cost sharing. It also prohibits employment-related discrimination based on reproductive health decisions.
let’s talk about
EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION
Emergency contraception (EC) reduces the chance of pregnancy after unprotected sex.
Common situations in which EC could be used include forgetting to take your birth control pill daily, having a condom break or slip off, or not using a birth control method during sex. It also can be used after a woman has experienced unwanted sex. Emergency contraception pills do not require a prescription and are available at most major retailers in the family planning aisle.
Using EC does not cause an abortion. This method prevents pregnancy from occurring. It should be used within 3-5 days (depending on the method) after unprotected sex to be effective. It does not work if a pregnancy has already occurred.
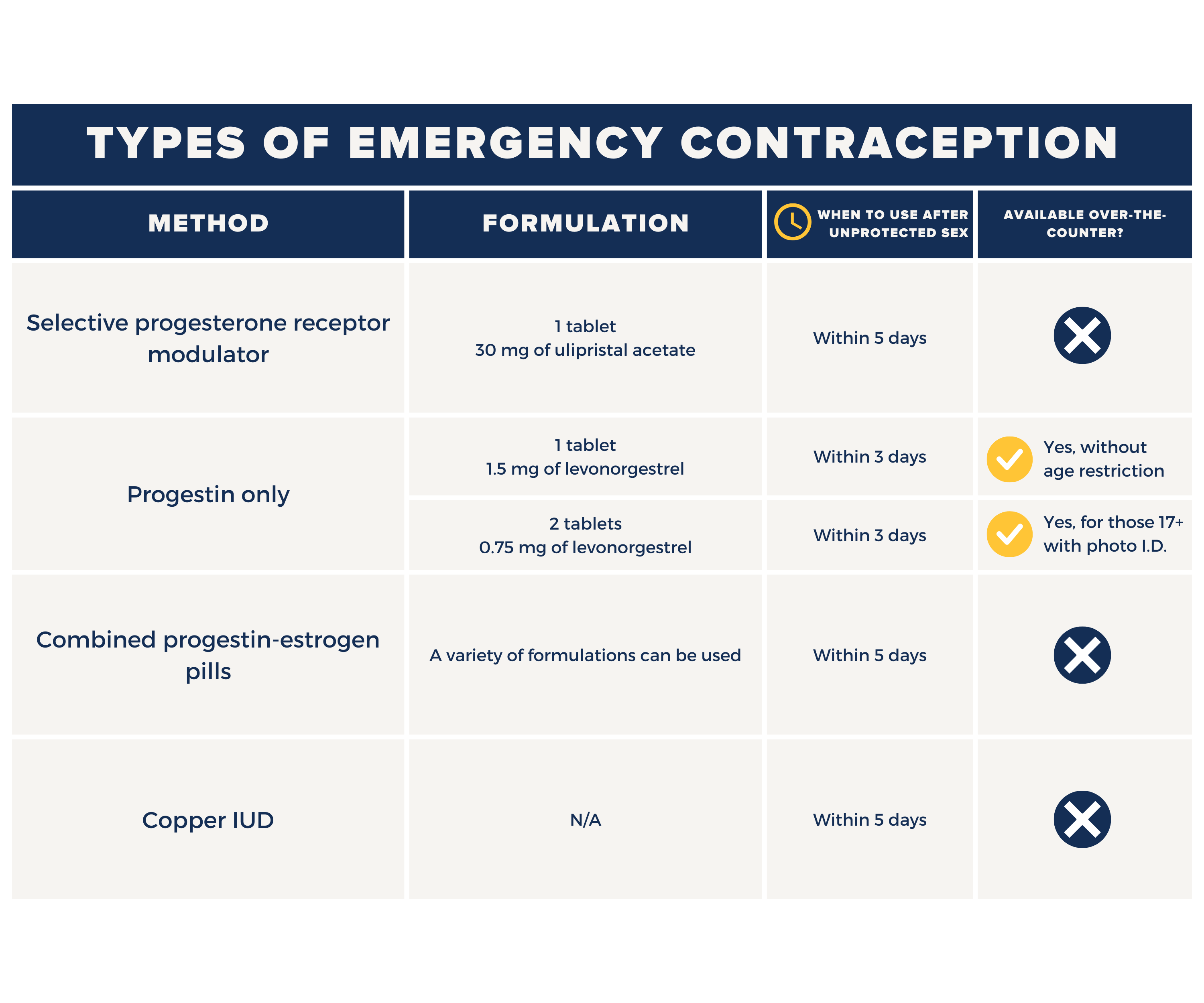
Types of Emergency Contraception
There are two types of EC: 1) the copper intrauterine device (IUD) and 2) EC pills.

IUD
Copper IUD
The IUD is a small, T-shaped device containing copper that is inserted by an obstetrician–gynecologist (OB-GYN) or other health care professional. The copper in the IUD prevents the sperm from fertilizing the egg. IUDs can also be left in place for up to 10 years for use as a primary form of birth control.
IUDs must be inserted by a health care provider.
$0 to $1,300 depending on coverage

IUD
Emergency Contraception Pills
Emergency Contraception (EC) pills can be used more than once during a single menstrual cycle. You should not rely on EC pills as a long-term birth control method. These pills are not as effective at preventing pregnancy as using a birth control method consistently and correctly. There also may be more side effects from frequent use of EC than from use of a standard birth control method. If you are not using birth control, talk with your OB-GYN or other health care professional about which method would work best for you.
The greatest advantage of the EC pill is that it can be bought at a pharmacy without a prescription.
$11 to $50
Emergency contraception is best used as soon as possible after unprotected sex.
Emergency Contraception Myths and Misperceptions
First
Myth #1: Emergency contraception causes abortions.
False. Emergency contraception, which is a formulation of progestin pills, does not cause an abortion. It prevents pregnancy from occurring. The sooner you take emergency contraception after unprotected sex (up to 5 days), the better your chance is of preventing pregnancy. Maximum recommended usage times vary depending on the method used.
Myth #2: Emergency contraception permanently disrupts your menstrual cycle.
False. Emergency contraception modifies ovulation to prevent pregnancy so your first period after taking EC could come early or late. It could also be lighter, heavier or spottier, but should return to normal for your next menstrual cycle.
Myth #3: You need a prescription to receive emergency contraception.
False. There are a couple methods that can be obtained without a prescription and purchased at most major retailers in the family planning aisle. Other methods, such as Ulipristal acetate and copper IUDs, do need a prescription though.
Myth #4: You can use emergency contraception as a long-term birth control method.
False. While emergency contraception has no effect on fertility or long-term health, there are better birth control methods that work to prevent pregnancy. You can decrease the stress of having an unplanned pregnancy by finding a reliable birth control method that’s best for you.
Myth #5: You will get really sick from taking emergency contraception.
False. Nausea is possible after taking an oral emergency contraception, but it isn’t always the case. Most people will not experience a bad case of nausea or sickness. If you do experience side effects, they usually resolve on their own.
Sources: Planned Parenthood, The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Food and Drug Administration, Bedsider, Healthcare.gov, HerLawyer 